Abstract
Introduction: Immunotherapy with Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cells (CAR-Τ) is a promising innovative treatment for refractory B cell malignancies offering a considerable chance for long-term survival in patients (pts) with an otherwise dismal prognosis. Since January 2020, two anti-CD19 CAR T cell products have been introduced into clinical practice in Greece: a) tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) for adults with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell Lymphoma (r/r DLBCL) including transformed follicular lymphoma (TFL), as well as for children or young adults with relapsed/refractory B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), and b) axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) for adults with r/r DLBCL including TFL and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL). The aim of this study was to present the real-world experience of the initial application of CAR T cell therapy in adult pts in Greece, with special focus on early toxicity and disease outcomes.
Methods: Data from all consecutive pts were collected from the two transplant centers which were initially accredited for CAR T cell therapies in adult pts: Evangelismos Hospital, Athens and George Papanicolaou Hospital, Thessaloniki. Between November 2019 and July 2021, 51 pts were referred for CAR T cell treatment. In 41 pts lymphocyte collection was performed and product manufacturing was successfully completed in 35; in 2 pts insufficient cell expansion was noted and in 4 manufacturing was terminated due to disease progression and patient death.
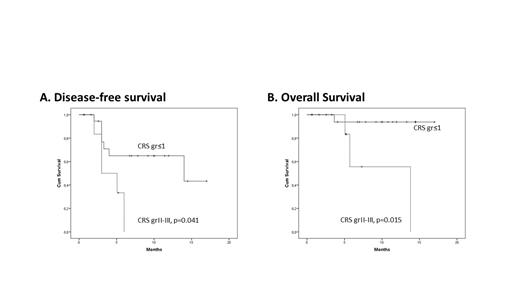
Results: From January 2020 until July 2021, CAR T cells were infused in 27 pts; 3 pts could not receive the product due to clinical deterioration/death and 5 pts are presently being scheduled for infusion. Of the 27 treated pts, 16 received tisagenlecleucel and 11 axicabtagene ciloleucel. The median age of infused pts was 49 (18-69) years. Diagnosis was DLBCL (n=16), PMBCL (n=3), TFL (n=2), B-ALL (n=6), and the median number of previous lines of treatment was 4 (2-5). Five pts with lymphoma had undergone autologous, and 4 pts with B-ALL allogeneic stem cell transplantation. In total 18/27 pts received bridging therapy, including radiotherapy (n=5), chemoimmunotherapy (n=9), steroids (n=3), and inotuzumab ozogamicin (n=1). The median time from leukapheresis to product delivery and infusion was 35 (15-81) and 59 (35-152) days, respectively. All pts received lymphodepleting therapy before CAR T cell infusion with combination of cyclophosphamide and fludarabine. For patient monitoring, prophylactic therapy and management of toxicity, the EBMT (Yakoub-Agha I, et al. Haematologica 2020) and MD Anderson (Neelapu S, et al. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2018) guidelines were adopted. Twenty-six pts developed neutropenia (grade II: 2, grade IV: 24) and 20 thrombocytopenia (grade I: 7, grade II: 3, grade III: 1, grade IV: 9), with a median duration of 11 (4-132) and 20 (3-150) days, respectively. Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity (ICANS) were noted in 21 (grade I: 8, grade II: 7, grade III: 6) and 5 (grade I: 3, grade III: 2) pts, respectively. Tocilizumab was administered for CRS according to guidelines, and steroids were additionally required for CRS and/or ICANS in 12 pts. In 2 pts, persistent ICANS necessitated further treatment with anakinra (n=2), siltuximab (n=1), and cyclophosphamide (n=1). Hypogammaglobulinemia was encountered in 14/27 pts. With a median follow-up of 7.3 (1-17) months, overall response rate was 48% with 12 (45%) pts being currently in complete remission (CR). No treatment related mortality was observed. Disease-free (DFS) and overall survival (OS) were 52% and 85.3% at 1-year, respectively. DFS and OS were significantly associated with baseline LDH levels (p=0.017 and 0.050, respectively) and grade II/III CRS (p=0.041 and 0.015, respectively, Figure).
Conclusions: Despite the limited experience in the real-world setting, CAR T cell therapy can be administered safely and may successfully rescue patients with DLBCL or B-ALL who lack alternative treatment options. Close monitoring of patients and prompt recognition and management of side effects are mandatory for achieving the benefits of therapy.
Baltadakis: WinMedica: Other: Travel Grants; Gilead: Other: Travel Grants; Genesis Pharma: Other: Travel Grants; Abbvie: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria, Other: Travel Grants; Astellas: Honoraria; Alexion: Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Baxalta Hellas: Other: Travel Grants. Gavriilaki: Pfizer Corporation: Research Funding; Gilead Corporation: Honoraria; Alexion, Omeros, Sanofi Corporation: Consultancy. Tzannou: Allovir: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company; Gileas: Honoraria. Anagnostopoulos: Abbvie: Other: clinical trials; Sanofi: Other: clinical trials ; Ocopeptides: Other: clinical trials ; GSK: Other: clinical trials; Incyte: Other: clinical trials ; Takeda: Other: clinical trials ; Amgen: Other: clinical trials ; Janssen: Other: clinical trials; novartis: Other: clinical trials; Celgene: Other: clinical trials; Roche: Other: clinical trials; Astellas: Other: clinical trials .